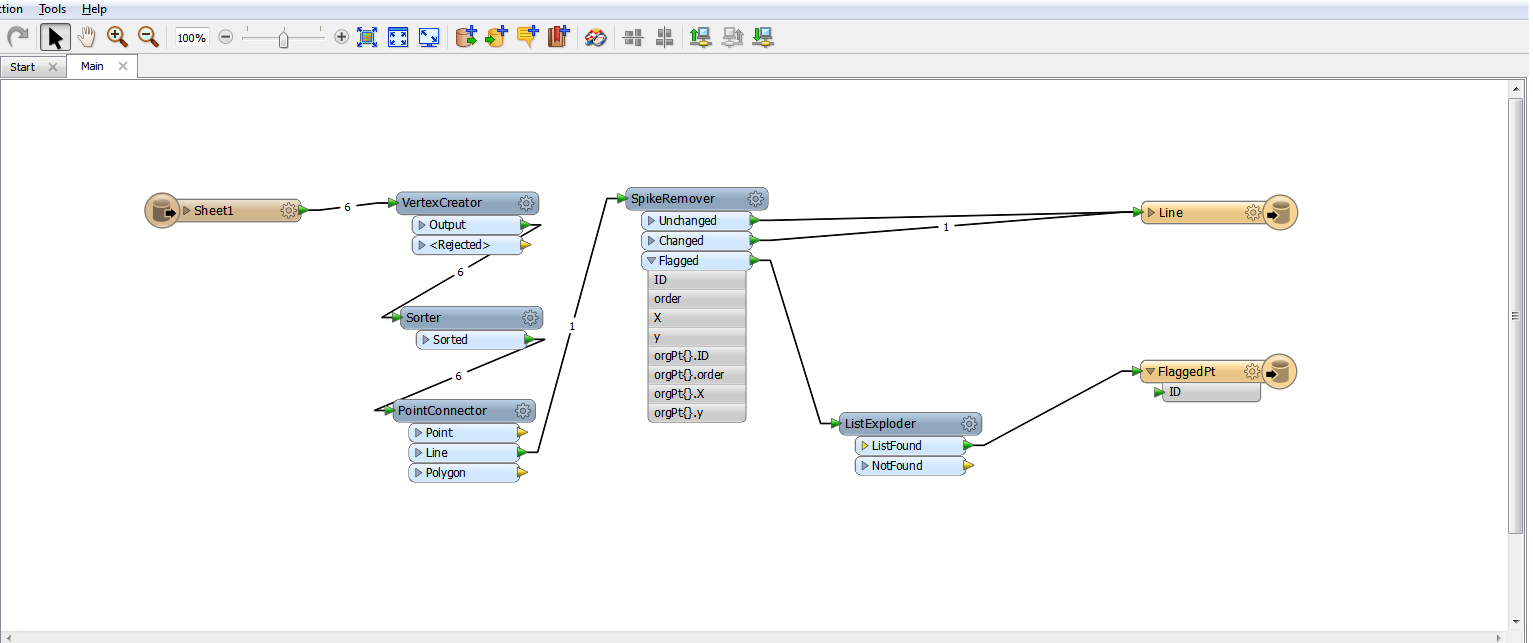
I have a workbench that creates a line from a source point file then uses a spike remover to remove erroneous points from the line. For the removed points I want to reassign them their original attribute from the source point file. I know the original attributes are stored in a list by the point connector, but I don't know how to assign the correct attribute to the correct point (using list manipulators I only seem to be able to assign ALL the original attributes to the point). How can I assign the original point attribute to the flagged point?
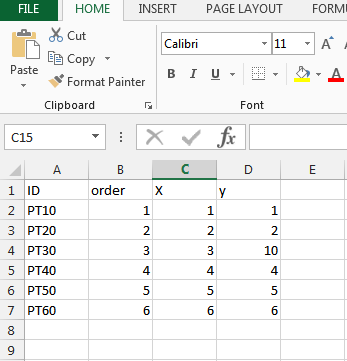
I have included a screen grab of (one of my many attempts) my workbench and some example excel data. In the example data PT30 is excluded from the line and output as expected, but I can't output it with "PT30" as the ID attribute.
Thanks!





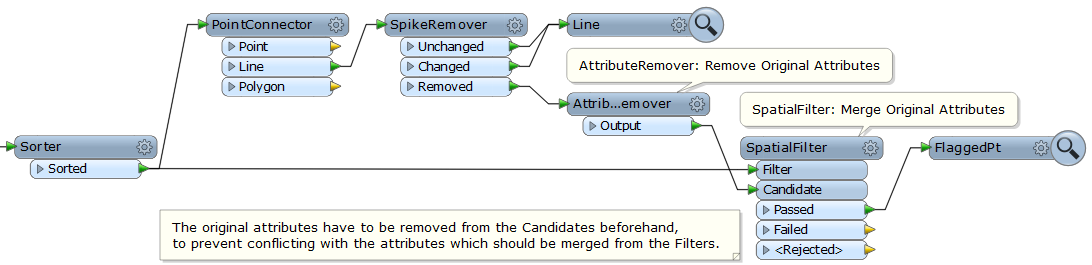
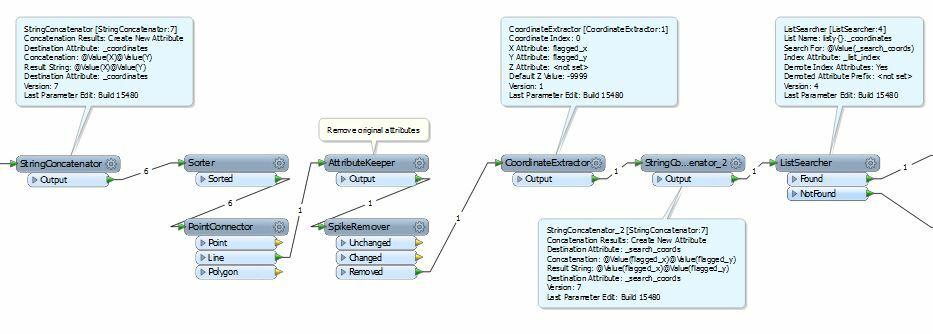 capture.jpg(58.0 kB)
capture.jpg(58.0 kB)